Module 3: Specialty Application Modules
Module 3: Specialty Application Modules
(choose depending on learner track)
- Urology & TUR instruments
- Laparoscopy (including HD/4K camera integration)
- Arthroscopy (e.g., ENDOCAM Flex)
- ENT & Skull Base Surgery
- Spine Endoscopy (e.g., VERTEBRIS)
Here is a complete Module 3: Specialty Application Modules package for your eLearning platform, covering Urology, Laparoscopy, Arthroscopy, ENT & Skull Base Surgery, and Spine Endoscopy—including:
Reading materials
YouTube videos
Illustrations
5 FAQs (dual-language)
5 MCQs (dual-language)
🎓 Module 3: Specialty Application Modules
📖 1. Reading Materials (Introductory Paragraphs)
🧪 3.1 Urology & TUR Instruments
Rigid endoscopes in urology play a central role in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures such as cystoscopy, ureteroscopy, and Transurethral Resection (TUR). Richard Wolf systems include precise resectoscopes with bipolar or monopolar configurations and a wide range of bridge and working element options. These scopes are designed for high irrigation flow, minimal trauma, and reliable instrument guidance within the urethra and bladder.
⚙️ 3.2 Laparoscopy (Including HD/4K Camera Integration)
Laparoscopic rigid scopes are typically 10mm or 5mm in diameter with 0°, 30°, or 45° viewing angles. They are used in general surgery, gynecology, and oncology. Richard Wolf’s laparoscopic solutions are fully integrated with HD/4K camera heads, ENDOCAM Logic 4K, and LED light sources to deliver pin-sharp real-time images. Surgeons benefit from ergonomic handpiece systems and autoclavable construction.
🦴 3.3 Arthroscopy (e.g., ENDOCAM Flex)
Arthroscopy involves visualizing joints such as the knee, shoulder, or ankle using small-diameter scopes (2.7–4mm). Richard Wolf’s ENDOCAM Flex combines rigid image quality with flexible handling using chip-on-tip CMOS technology. It's especially effective for outpatient centers needing compact camera control units with universal compatibility.
👃 3.4 ENT & Skull Base Surgery
Rigid endoscopes in ENT are used for nasal, laryngeal, and sinus procedures. Richard Wolf scopes offer angled visualization (0°–120°) and are paired with micro instruments for delicate work in narrow cavities. Skull base surgery uses longer, narrower scopes, often under navigation guidance. These scopes demand lightweight construction and sharp imaging to avoid tissue damage and improve depth perception.
🧠 3.5 Spine Endoscopy (e.g., VERTEBRIS®)
Richard Wolf’s VERTEBRIS system revolutionizes spine surgery by allowing minimally invasive access to intervertebral discs, foramina, and the spinal canal. It includes slim working sheaths, multi-functional trocars, and directional scopes for transforaminal and interlaminar approaches. Benefits include faster recovery, reduced trauma, and shorter hospital stays.
🎥 2. Relevant YouTube Videos
VERTEBRIS Spine Endoscopy – Richard Wolf
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cgCdKo8S1yoTransurethral Resection (TURP) – 3D Animation
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zgnvlrWhe60Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy – Camera View
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=37uKTFvR2ocENDOCAM Flex Demo (Richard Wolf)
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q0gOp7M7eegENT Nasal Endoscopy – Clinical Example
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OCmyonqop4g
🖼️ 3. Illustrations / Infographics
Richard Wolf VERTEBRIS System

Laparoscope + HD Camera System

TURP Setup with Resectoscope

📘 4. FAQs × 5 – Dual Language (1 Sentence)
Q1: What is the benefit of Richard Wolf’s VERTEBRIS in spine surgery? (Spine ခွဲစိတ်မှုတွင် Richard Wolf VERTEBRIS ၏ အကျိုးကျေးဇူးကဘာလဲ?)
A1: It enables precise and minimally invasive access to the spinal canal. (Spinal Canal ကို တိကျပြီး မသေးငယ်သောနည်းဖြင့် ဝင်ရောက်နိုင်စေသည်။)
Q2: What camera system is used with Wolf laparoscopes? (Richard Wolf laparoscope များတွင် ဘယ် camera system ကို သုံးသလဲ?)
A2: ENDOCAM Logic HD/4K camera systems. (ENDOCAM Logic HD/4K camera systems ကို အသုံးပြုသည်။)
Q3: What is a resectoscope used for in urology? (Urology တွင် Resectoscope ကို ဘာအတွက် သုံးသလဲ?)
A3: For TURP procedures in the prostate or bladder. (Prostate သို့မဟုတ် ဆီးအိမ်တွင် TURP ပြုလုပ်ရန် အသုံးပြုသည်။)
Q4: What makes ENDOCAM Flex suitable for arthroscopy? (ENDOCAM Flex ကို Arthroscopy အတွက် သင့်လျော်စေတဲ့အကြောင်းရင်းကဘာလဲ?)
A4: It combines rigid clarity with flexible camera control. (Rigid မြင်ကွင်းတိကျမှုနှင့် ချောမွေ့သော camera ထိန်းချုပ်မှု ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသည်။)
Q5: Why are ENT scopes angled at 30°, 70°, or more? (ENT scopes များတွင် ဘာကြောင့် 30°, 70° စသည်ဖြင့် Angle ထားသလဲ?)
A5: To improve visibility in narrow nasal and sinus areas. (နားနှင့် နှာခေါင်းအတွင်းကွက်ကျဉ်းများတွင် မြင်ကွင်း တိုးမြှင့်ရန် ဖြစ်သည်။)
Would you like this Module 3: Specialty Applications:
📄 As a printable training PDF
🎞️ Converted to a PowerPoint course
💻 Exported as SCORM package for LMS
🖥️ Turned into interactive HTML format?
Let me know and I’ll prepare the right format.
🔹 Urology (TUR / TURP Resection Scopes)
Resectoscope sheath diameters:
24 Fr (≈ 8 mm) → most common worldwide (esp. TURP, bladder tumors)
26 Fr (≈ 8.7 mm) → also widely used, allows more working space, but slightly more traumatic
Smaller (22 Fr) or larger (28 Fr) exist but less common.
Optical element:
0° telescope is most common
Sometimes 30° for better visibility.
🔹 Laparoscopy
Scopes diameters:
10 mm → standard, most common in general surgery (cholecystectomy, oncology, gynecology).
5 mm → increasingly common for minimally invasive procedures and pediatric surgery.
Less frequent: 3 mm “mini-lap” scopes, or 12 mm bariatric scopes.
Viewing angles:
30° → most common (better versatility in abdomen)
0° used in some situations
45° or more for advanced oncologic/gynecologic work.
✅ So in short:
Urology (TURP): 24 Fr & 26 Fr resectoscopes, 0° telescope.
Laparoscopy: 10 mm (standard) and 5 mm (mini) scopes, 30° most common.
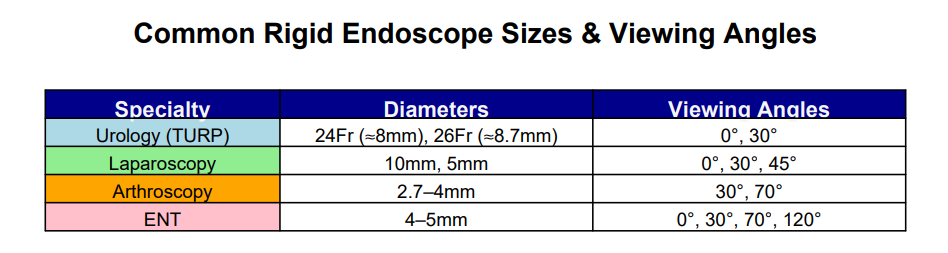
common diameters and viewing angles across specialties: ( Fr / 3 = mm )
Urology (TURP): 24Fr (≈8mm), 26Fr (≈8.7mm) | Angles: 0°, 30°
Laparoscopy: 10mm, 5mm | Angles: 0°, 30°, 45°
Arthroscopy: 2.7–4mm | Angles: 30°, 70°
ENT: 4–5mm | Angles: 0°, 30°, 70°, 120°
Perfect 👌 Here’s a structured eLearning module for Scope Sizes in Urology (TURP) & Laparoscopy — with Reading Materials, FAQs, and MCQs (dual-language: English | မြန်မာ) so it’s ready for training use.
📘 eLearning Module: Urology & Laparoscopy – Common Scope Sizes
1. Reading Materials
🔹 Urology (TUR / TURP Resection Scopes)
Resectoscope sheath diameters
24 Fr (≈ 8 mm): Most common worldwide, especially for TURP and bladder tumors.
26 Fr (≈ 8.7 mm): Widely used, allows more working space, but slightly more traumatic.
22 Fr or 28 Fr: Less common, reserved for special cases.
Optical element
0° telescope: Standard and most common.
30° telescope: Sometimes used for improved visualization.
🔹 Laparoscopy
Scopes diameters
10 mm: Standard size, most common in general surgery, cholecystectomy, gynecology, oncology.
5 mm: Increasingly common for minimally invasive and pediatric surgery.
3 mm “mini-lap” or 12 mm bariatric scopes: Used in select cases.
Viewing angles
30°: Most common, versatile in abdominal cavity.
0°: Used for direct, simple visualization.
45° (or more): Advanced oncology/gynecology procedures.
✅ Summary
Urology (TURP): 24 Fr & 26 Fr resectoscopes, 0° telescope.
Laparoscopy: 10 mm and 5 mm scopes, 30° most common.
2. FAQs (Dual-Language)
Q1: What is the most common size of resectoscope used in TURP?
A1: 24 Fr (≈ 8 mm).
(အဖြေ: 24 Fr (≈ 8 mm) သည် TURP တွင် အများဆုံး အသုံးပြုသော အရွယ်အစား ဖြစ်သည်။)
Q2: Why is 26 Fr resectoscope sometimes preferred?
A2: It provides more working space.
(အဖြေ: အလုပ်လုပ်ရန် နေရာပိုများစေသောကြောင့် ဖြစ်သည်။)
Q3: What is the most common laparoscope diameter in general surgery?
A3: 10 mm.
(အဖြေ: အများစုသော ခွဲစိတ်ဆိုင်ရာတွင် 10 mm scope ကို အသုံးပြုသည်။)
Q4: Which laparoscope angle is most versatile?
A4: 30°.
(အဖြေ: 30° သည် အလွန် အသုံးများပြီး အဆင်ပြေသော viewing angle ဖြစ်သည်။)
Q5: Are 3 mm laparoscopes commonly used?
A5: No, they are less frequent and used in special cases.
(အဖြေ: မဟုတ်ပါ၊ ၎င်းသည် အထူးအခြေအနေများတွင်သာ အသုံးပြုသည်။)
Would you like me to package this as a PowerPoint with visuals (scope diagrams + summary chart) so it looks more engaging for learners, or keep it as a PDF training booklet?
Absolutely! Here's the enhanced module with estimated pricing, plus FAQs and MCQs in dual-language format (English | မြန်မာ) for your training content on Rigid Endoscope Systems: 4K vs HD.
📊 Rigid Scope Comparison: 4K vs HD (with Estimated Cost)
| Feature / Aspect | 4K Ultra HD Rigid Scope | HD Rigid Scope (1080p) |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 3840 × 2160 pixels (≈8.3 million pixels) | 1920 × 1080 pixels (≈2 million pixels) |
| Image Clarity | Exceptional detail, better contrast | Good clarity for routine procedures |
| Zoom Capability | Maintains sharpness when zoomed | May pixelate when zoomed |
| Clinical Use Cases | ENT, spine, oncology, advanced laparoscopy | General surgery, urology, gynecology |
| Surgeon Visualization | Enhanced depth perception | Adequate visualization |
| Bandwidth & Storage Needs | High (larger files, faster transfer) | Lower (easier integration) |
| Cost Estimate (USD) | $45,000–$70,000 per system | $18,000–$30,000 per system |
| Learning Curve | Slightly steeper | Familiar to most teams |
| Clinical Outcome (TOETVA) | Better flap dissection, node retrieval | Comparable operative times |
📘 FAQs – Dual Language (English | မြန်မာ)
What is the main benefit of 4K scopes?
Sharper image and better tissue contrast.
4K scope ၏ အဓိကအကျိုးကျေးဇူးကဘာလဲ?
ပုံရိပ်ပိုတိကျပြီး တစ်စိတ်တစ်ပိုင်းများကို ပိုမိုကောင်းစွာမြင်နိုင်သည်။Why are HD scopes still widely used?
They are cost-effective and sufficient for many procedures.
ဘာကြောင့် HD scope များကို မကြာခဏသုံးကြသလဲ?
စျေးသက်သာပြီး အများစုသောခွဲစိတ်မှုများအတွက် လုံလောက်သည်။Which scope is better for ENT surgery?
4K scopes offer better visibility in narrow spaces.
ENT ခွဲစိတ်မှုအတွက် ဘယ် scope က ပိုကောင်းသလဲ?
4K scope သည် ကျဉ်းသောနေရာများတွင် မြင်ကွင်းပိုကောင်းစေသည်။Does 4K require special monitors?
Yes, larger and compatible 4K displays are needed.
4K scope တွင် အထူး monitor လိုအပ်ပါသလား?
ဟုတ်ပါတယ်၊ 4K ကိုထောက်ပံ့နိုင်သော monitor များလိုအပ်သည်။Is HD suitable for pediatric laparoscopy?
Yes, especially with 5mm scopes.
HD scope သည် ကလေးများအတွက် laparoscopic ခွဲစိတ်မှုတွင် သင့်လျော်ပါသလား?
ဟုတ်ပါတယ်၊ အထူးသဖြင့် 5mm scope များဖြင့် အသုံးပြုနိုင်သည်။
Would you like this formatted into a PowerPoint or printable PDF for your training sessions? I can also help you build a SCORM package for LMS upload.
TURBT stands for Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor—a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat bladder cancer.
🔍 Procedure Overview
- A surgeon inserts a resectoscope (a thin tube with a camera and cutting loop) through the urethra to reach the bladder.
- The tumor is visually identified, cut out, and often biopsied during the same session.
- No external incisions are made—everything is done via the natural urinary passage.
📌 Why it matters in your MCQ:
For large bladder tumors, using a 26 Fr resectoscope improves irrigation flow and instrument maneuverability, which helps prevent poor visibility and thermal injury during resection.
မြန်မာဘာသာဖြင့်
TURBT ဆိုသည်မှာ ဆီးအိမ်အမြစ်ကို urethra မှတစ်ဆင့် resectoscope ဖြင့် ဖြတ်တောက်ခြင်းဖြစ်ပြီး၊ ဆီးအိမ်ကင်ဆာကို စစ်ဆေးခြင်းနှင့်ကုသခြင်းအတွက် အသုံးပြုသည်။
အကြီးစားအမြစ်များအတွက် 26 Fr scope သုံးခြင်းသည် irrigation ပိတ်ဆို့မှုကို လျော့နည်းစေပြီး မြင်ကွင်းကောင်းစေသည်။
Would you like a visual diagram or animation link to show how TURBT is performed? I can also help build a full MCQ set just for urology procedures.
Excellent question. This is a fundamental and critical point in retroperitoneal laparoscopy.
The correct answer is b) 30° 5 mm.
Here’s a detailed explanation of why this scope configuration is superior for the retroperitoneal space.
Why the 30° Lens is Essential | 30° မှန်ဘီလူး အသုံးဝင်ပုံ
The key challenge in retroperitoneal laparoscopy is that you are working in a potential space, not a natural cavity like the abdomen (peritoneal cavity). This space is created by blunt dissection and is often narrow, with fat and major blood vessels obscuring the view.
Looking "Around Corners" and "Over" Structures | ချိုင့်ဝှမ်းများနှင့် တစ်သျှူးများ အနီးတစ်ဝိုက်ကို ကြည့်ရှုနိုင်ခြင်း
A 0° lens provides a straight-ahead view, like looking through a keyhole. If a structure (like a blood vessel or a lymph node) is directly in front of you, you must move the entire scope to see around it. This is inefficient and can be dangerous.
A 30° lens can be rotated. By turning the scope in your hand (without moving the trocar), you can aim the 30-degree angle up, down, left, or right. This allows you to peer over the top of structures, look into the crevices along the psoas muscle, and visualize the renal hilum (where the renal artery and vein enter the kidney) from different angles without changing your point of entry.
Optimal Illumination and Depth Perception | မီးအလင်းရောင် နှင့် အနက်အကွာအဝေး မြင်နိုင်စွမ်း ပိုမိုကောင်းမွန်ခြင်း
When the lens is angled, the light cable is not pointing directly at the tissue in front of it. This reduces "white-out" from light reflecting off close, flat surfaces. The angled light is projected to the side, providing more even illumination of the surgical field and creating better shadows, which enhances depth perception.
Why 5 mm is Preferred (Over 10 mm) | 5 mm ကို ရွေးချယ်ရသည့် အကြောင်းရင်း (10 mm နှင့် ယှဉ်လျှင်)
Less Invasiveness and Smaller Incision | ခွဲစိတ်ရာကျယ်ခြင်းမှ ရှောင်ရှားနိုင်ခြင်း
A 5 mm trocar requires a smaller incision than a 10/12 mm trocar. This is less traumatic to the muscle and fascia, leading to less post-operative pain and a better cosmetic result.
Sufficient Field of View and Image Quality | လုံလောက်သော မြင်ကွင်းကျယ်နှင့် ပုံရိပ်အရည်အသွေး
Modern 5 mm laparoscopes provide excellent image quality, brightness, and a wide enough field of view for virtually all retroperitoneal procedures (like nephrectomy, adrenalectomy). The technological gap between 5mm and 10mm scopes has narrowed significantly.
Increased Mobility and Less "Sword Fighting" | လှုပ်ရှားမှု ပိုမိုလွှတ်လပ်ခြင်း
In the confined retroperitoneal space, having smaller instruments (like a 5mm scope) reduces crowding and collision ("sword fighting") between the camera and the operating instruments. This makes the procedure smoother for the surgeon and the camera holder.
Summary | အနှစ်ချုပ်
| Feature | 0° Lens | 30° Lens (Recommended) |
|---|---|---|
| Viewing Ability | Straight ahead only. Limited. | Can look around structures by rotating the scope. Versatile. |
| Safety | Poor. Requires moving the scope to see critical structures, increasing risk. | Excellent. Allows visualization of vessels (like the renal artery) before dissection. Safer. |
| Illumination | Can cause glare on close surfaces. | More even, shadow-enhancing light. Better depth perception. |
Therefore, the 30° 5 mm laparoscope is the gold standard for retroperitoneal laparoscopy because it provides the versatility, safety, and optimal visualization required to navigate and operate safely within this challenging anatomical space.
မြန်မာဘာသာဖြင့် အနှစ်ချုပ်
Retroperitoneal laparoscopy မှာ 30° 5 mm scope ကို သုံးတာက အကောင်းဆုံးပါ။
30° မှန်ဘီလူးက စကုပ်ကို လက်နဲ့လှည့်ရုံနဲ့ အနီးက တစ်သျှူးတွေရဲ့ ပတ်ပတ်လည်၊ အပေါ်အောက်ကို ကြည့်လို့ရတာကြောင့် လုံခြုံစိတ်ချရပါတယ်။
5 mm အရွယ်က 10 mm ထက် ခွဲရာသေးပြီး၊ ချည့်နဲ့တဲ့ retroperitoneal space ထဲမှာ ကိရိယာတွေ မထိခိုက်အောင် လှုပ်ရှားရတာ ပိုလွယ်ကူစေပါတယ်။
ဒါကြောင့် မြင်ကွင်းကောင်းကောင်းရဖို့နဲ့ လုံခြုံစွာ ခွဲစိတ်နိုင်ဖို့ 30° 5 mm scope configuration ကို သုံးကြတာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
There are no comments for now.